Samsung’s QNED, will make a sensation in the TV and display markets?
QNED (Quantum dot nanorod LED), which is known to be under development by Samsung, is becoming a hot issue in the display industry in 2020.
With the emergence of micro LEDs, followed by CRTs, PDPs, LCDs, and OLEDs as TV displays, the industry is interested in whether QNED could be another new technology.
Samsung Display is known to stop the LCD business and invest 13.1 trillion won as an alternative to do the QD-OLED business. In this situation, attention is being focused because the development of QNED can act as another variable in the future of Samsung Display’s large display business.
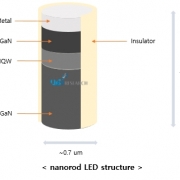
QNED uses oxide TFT and QD (quantum dot) -CF (color filter) technologies used in QD-OLED manufacturing. On the other hand, the pixel material that emits light is characterized by being changed to a nano-sized bar-type LED (nanorod LED), unlike OLED emitting materials. The pixel manufacturing technology, which is the core technology of QNED manufacturing, is a method of spraying nanorod LEDs dispersed in a solution into a pixel area by an ink jet method and arranging them in a self-align method by an electric signal.
UBI Research published a report that analyzed the structure and manufacturing technology of QNED based on the patented technology filed by Samsung Display. This report is structured to quantitatively analyze QNED-related patents filed by Samsung Display, so that QNED’s technology completeness and mass productivity can be known.