Yi Choong Hoon Yi, Chief Analysis / UBI Research
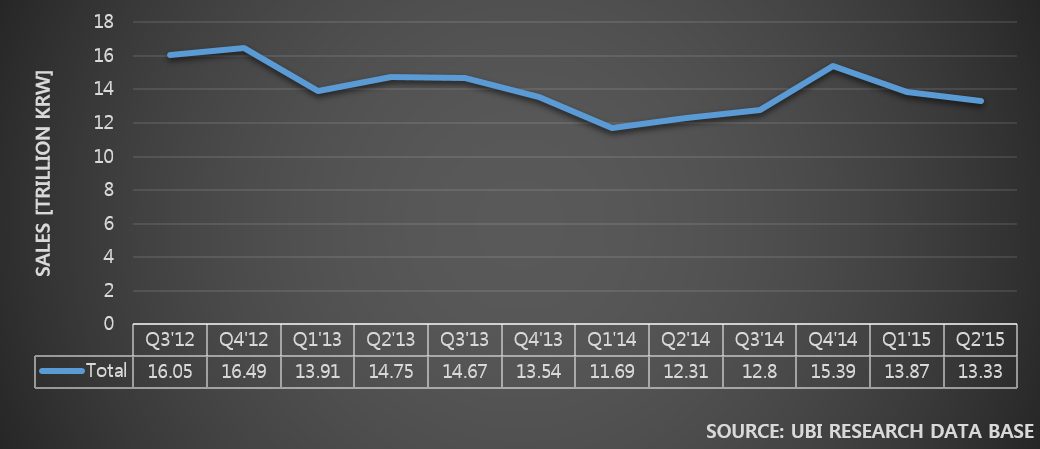
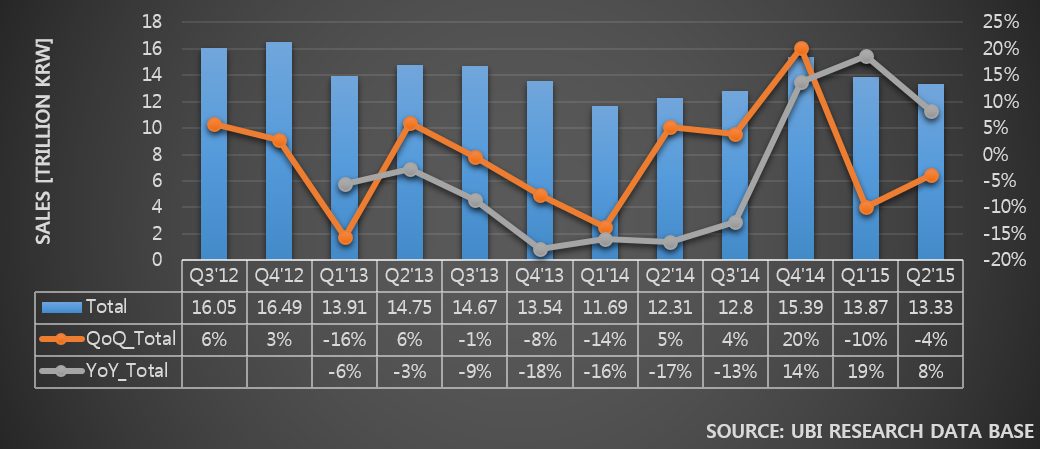
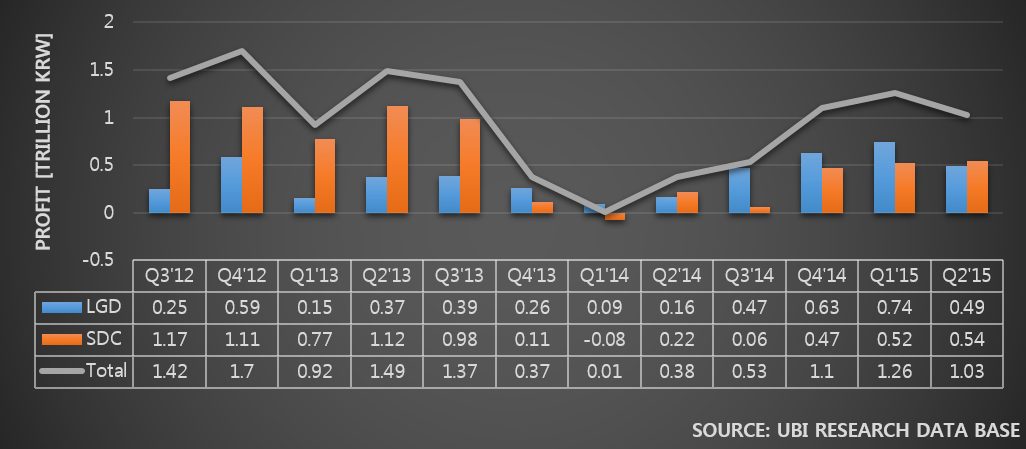
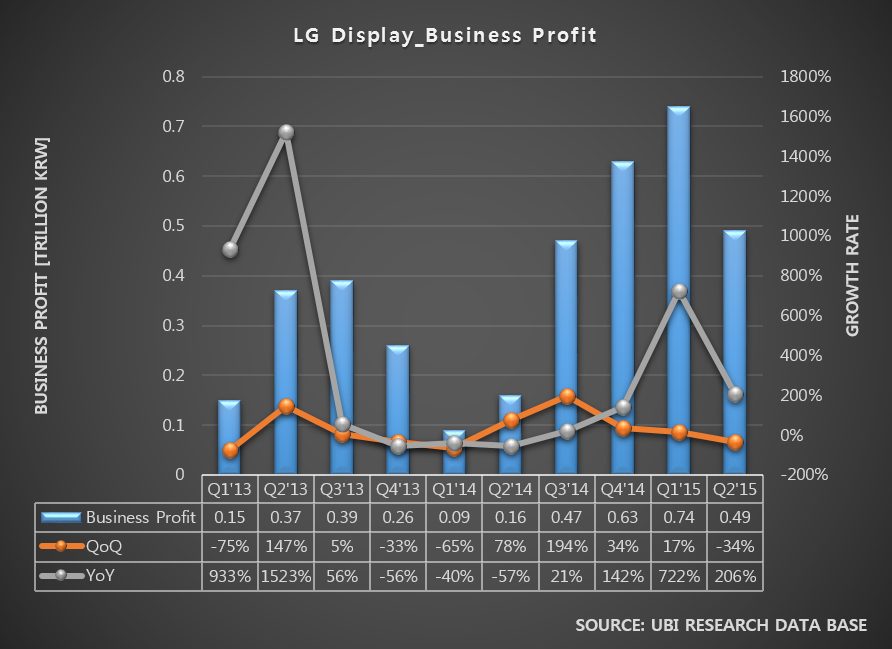
In 2014, as the revenue and business profit fluctuated greatly per quarter, Samsung Display carried out management evaluation with BCG. One of the conclusions is known to be Gen10 LCD investment together with large area OLED for TV investment.
Gen10 LCD line investment is seen to be a countermeasure against Chinese display companies that continue their aggressive investment and display industry that is expanding in information society. It is analyzed that the large area OLED line investment is to prepare for the OLED TV market growth which has superior picture quality compared to LCD and to control their biggest rival company LG’s WRGB OLED TV market expansion which is maintaining their investment.
These two plans are obvious conclusions that any display expert can draw.
However, any experts who know Korea’s display would recognize that Gen10 LCD line investment is not suitable for Korea. This is because even if Korea expands the market share by investing in Gen10 LCD line they will still be weak against Chinese display companies in price. Korean display companies only sell high quality goods and 90~95% is the limit of yield rate. In comparison, in China the size of the population who can easily purchase expensive high quality TV and the consumers who demands lower priced goods are both huge; faulty display panels have a place in Chinese market. Chinese display companies can also sell lower quality panels through close relationship with lower price TV production companies with factories in China. Theoretically, this can lower the panel price as yield rate close to 100% can be achieved. Furthermore, support from Chinese government and cheap factory construction cost increases price competitiveness of Chinese display companies even more.
The reason Japanese display companies had no choice but to give up LCD market to Korean display companies was also because they could not continue LCD investment with their difficulty in price competitiveness. Although Sharp vigorously continued investing until Gen10 line, the result was decision to sell small size LCD line for mobile device due to the accumulated deficit.
If Samsung Display decides on Gen10 investment, it is highly likely that they will follow similar path to Sharp’s, increasing the risks rather than sales. It is more effective for Samsung Electronics to lead TV industry using Chinese companies’ cheap LCD panel with good definition rather than producing TV using expensive Korean LCD panels with good picture quality. The fact that there are no comments regarding Gen10 investment within Samsung Display can be interpreted that there are experts with good understanding of display industry.
Unlike the current Samsung Elec. business strategy where the focus is exclusively on quantum dot technology applied LCD SUHD TV, the large size line investment decision for OLED TV production is a conclusion that requires change in Samsung’s business strategy. In CES 2015, Samsung Elec. exhibited SUHD TV and OLED TV in comparison and highlighted LCD TV’s superiority in picture quality. If SUHD TV is more competitive than OLED TV, it is not worth investing any further.
However, the story is different in smart phone market. This is because Samsung Elec.’s flagship model Galaxy series all use AMOLED. One of the differentiation strategies that Samsung Elec. is using when selling Galaxy series is OLED. Wireless department of Samsung Elec. expanded the market share to 20% using the smart phone with the word ‘OLED’ attached. Most recently, flexible OLED applied Galaxy S6 Edge is hugely popular.
Samsung Elec.’s smart phone business department, IM, is recording twice the amount of revenue of VD business department that produces TV. Therefore that VD department’s marketing method of emphasizing OLED has worse definition than LCD is contradictory since IM department is marketing their product by valuing the superior picture quality of OLED over LCD. If QD-LCD is good then obviously the panel for Galaxy S series also has to be replaced to QD-LCD. Insisting that OLED has better picture quality in smart phone and LCD is superior in TV is mutually incompatible. This kind of dual behavior could result in Samsung Elec.’s rationales to be considered as ones by the boy who cried wolf. For the future expansion of Samsung Elec.’s smart phone market, VD department also has to produce OLED TV and establish the equation of ‘Samsung Elec. = OLED’ in order to complete the business strategy.
This is the reason Samsung must undertake OLED TV.
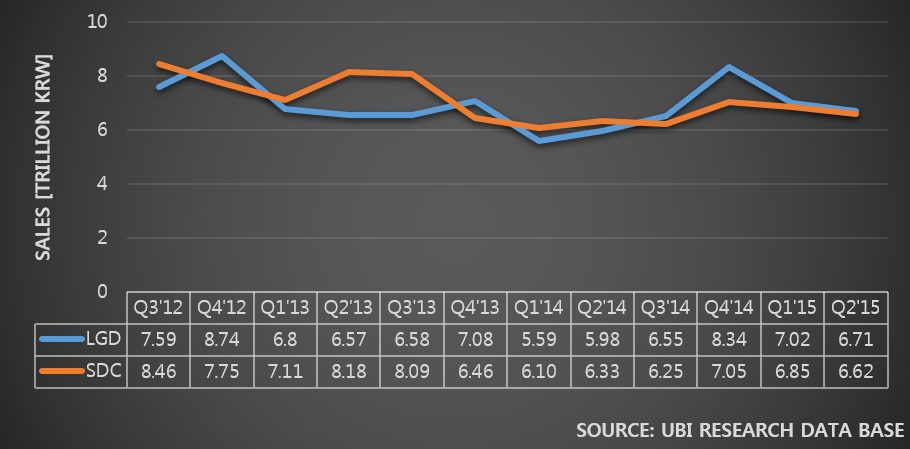
Nevertheless, problems are numerous. OLED TV produced by Samsung Elec. in 2013 was deemed to be marginally inferior in terms of completeness and picture quality compared to LG Electronics’ OLED TV by UBI Research’s Picture Quality Analysis Report and an article in OLEDNET. Since then Samsung Elec. halted OLED TV production practically acknowledging that their own OLED TV could not compete against LG Elec.’s product. The reason for this could be attributed to TV’s lower completeness but the fundamental reason lied in the fact that Samsung Display’s RBG OLED panel production method and characteristics could not compete against LG Display’s WRGB OLED in picture quality and competitiveness.
RGB OLED for Large area uses fine metal mask similar to small size AMOLED, and therefore OLED panel production is not possible using Gen8 mother glass and has to use evaporator for Gen8 glass cut into 6. As LG Display’s WRGB OLED manufactures pixels using white OLED with color filter fine metal mask is not required which allows for OLED panel production in Gen8 without cutting. Compared to the fact the rival company LG Display is using 1 Gen8 evaporator, Samsung Display requires 6 evaporators. The increased number of evaporators obviously leads to an increase in investment cost and the panel production cost cannot but be higher than LG Display.
Even in TFT production cost, Samsung Display is weaker in comparison to LG Display. LTPS-TFT process used by Samsung Display requires 8~9 mask processes but LG Display is using oxide TFT which needs 4~5. Therefore, it has an advantage of minimizing the investment cost when LCD line is transformed to OLED line. For Samsung Display to transform existing LCD line to OLED line, they have to add a huge amount of capital to the LTPS-TFT production. If they transform the existing 200K LCD factory to OLED line, the capa. also decreases to 90K, but LG Display can maintain the 200K volume without any loss. When OLED is produced transforming the existing LCD line, LG Display does not need additional factory construction but it is calculated that Samsung Display has to build another factory of equal size.
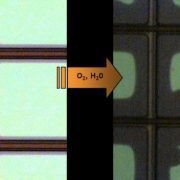
In encapsulation process, LG Display, which uses hybrid encapsulation technology, remains advantageous. This completes the OLED panel production by attaching adhesive film laminated metal foil on top of passivation which is a moisture proof structure made with 2~3 layers of passivation after OLED device production. The OLED panel for TV that was mass produced by Samsung Display in 2013 also used hybrid encapsulation structure. The difference was that the top substrate was glass. However, as Samsung Display was accused by LG Display for appropriating their encapsulation technology, Samsung is currently developing dam & fill method of hybrid encapsulation technology. Samsung Display’s dam & fill hybrid encapsulation technology shares the part of forming passivation layer on top of device with LG Display. However, after that Samsung Display applies curing agent using ODF (one drop filling) method to the dam made with organic materials on the outside of the panel. They then attach the glass substrate and harden. Although it would be better if the dam production could occur simultaneously as PDL (pixel define layer) process, generally as PDL layer is on top of TFT and dam structure is on the outside of the panel, height difference could develop leading to difficulty in upper substrate attachment. Furthermore, if the dam height is lower than PDL’s, it is unfavorable for the curved design which is the latest TV trend. Accordingly, if the dam formation process ensues after passivation is complete, further mask process is necessary which increases cost due to the added equipment investment. Samsung Display’s encapsulation process is a continuous operation whereas LG Display’s process can attach the coring film to the metal foil and send the selected high quality products to attachment process; for yield rate management, LG Display is better suited. Dam & fill method has to fill the liquid curing resin first before the attachment of upper substrate. This means that several hundreds of um thickness of glass substrate attachment is more appropriate rather than attaching metal foil of dozens of um thickness. In that case, metal foil cannot be used and additional heat sink materials are required. In encapsulation process, LG Display technology is better for mass production and has an advantage of being able to lower the production cost.
In conclusion, for Samsung Display to re-enter OLED panel for TV industry, rather than using their existing technology of LTPS-TFT, RGB OLED, and damn & fill encapsulation, it is better to use the technology being used by LG Display such as oxide TFT structure, WRGB OLED structure and lamination method of encapsulation structure that uses adhesive film.
To challenge large area OLED panel industry again, Samsung Display placed the existing large area OLED team under research lab led by their top OLED expert SungChul Kim. Although there has been no official discussion regarding OLED panel production technology directional course, using the same technology as LG Display’s would be advisable in order to succeed.
In terms of resources, Samsung Display, with their many years of OLED panel mass production experience and several thousands of top quality OLED engineers, is superior compared to LG Display.
Only the patents and decision making processes are left.