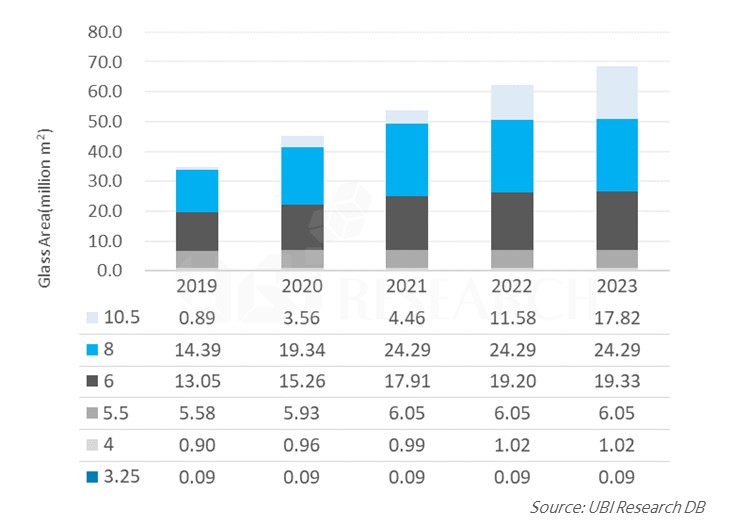
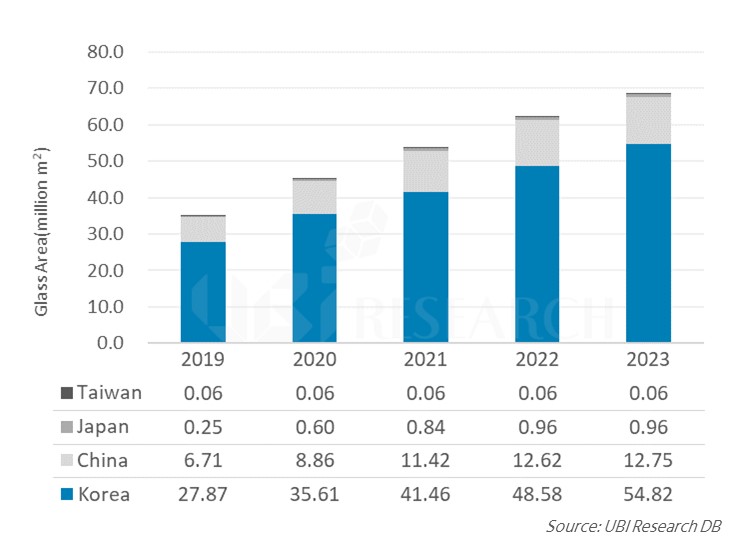
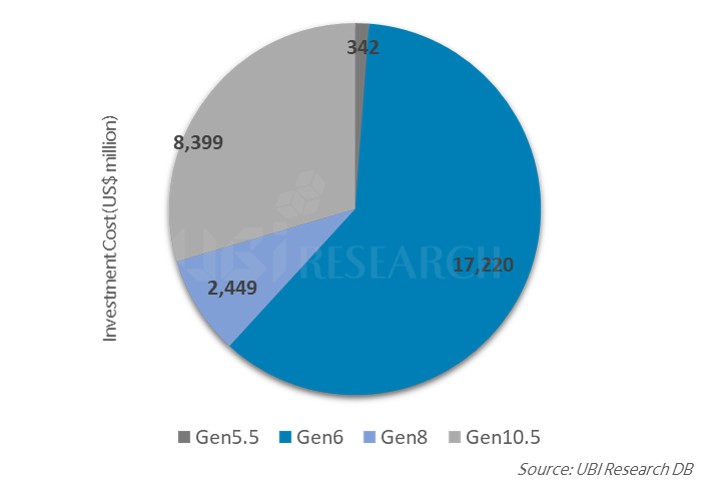
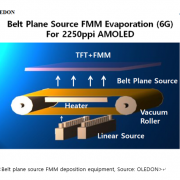
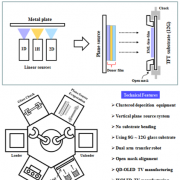
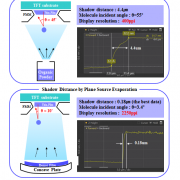
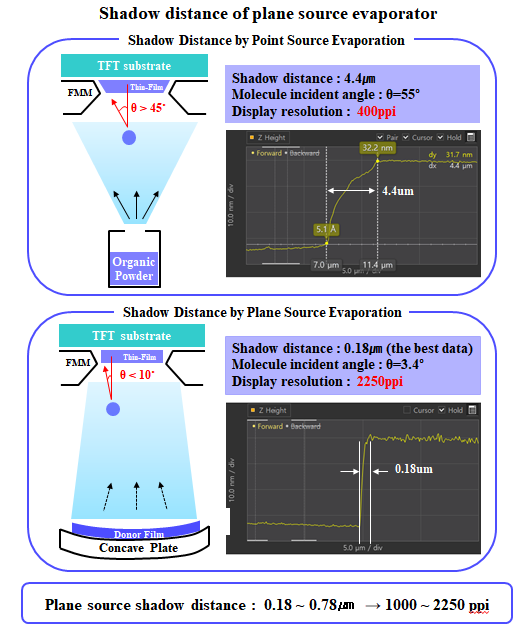
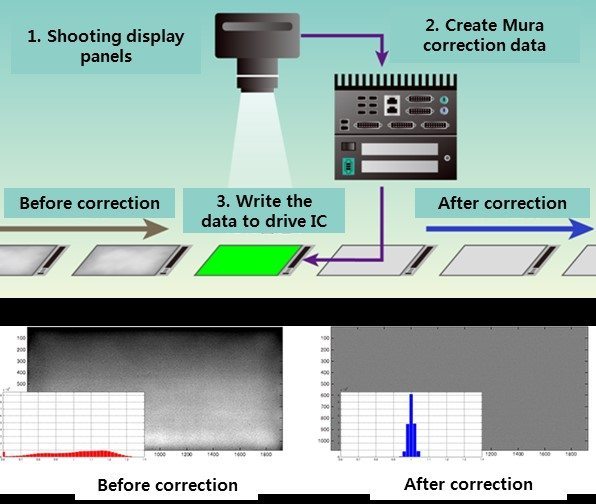
78.6 tons of OLED emitting material demand increased by 5.6% in 2020
According to the 2020 OLED emitting material report published by UBI Research, the demand for emitting materials in 2020 is 78.6 tons, which is 4.2 tons higher than last year’s 74.4 tons. The material used for OLEDs for smartphones and mobile devices is 62.9 tons, and the OLED emitting material for TVs is expected to be 15.7 tons.
In 2019, the total emitting material market was totaled at $ 1.28 billion, and 43% of the total amount was purchased from Samsung Display. It was found that the amount purchased by LG Display was 19.4% and the BOE was 11.6%. LG Display’s purchase of emitting materials accounted for 60.8% of TV use. The order of purchase of emitting materials for mobile devices is in order of Samsung Display, BOE, and LG Display. This is because BOE has a large amount of OLED production for mobiles after Samsung Display.

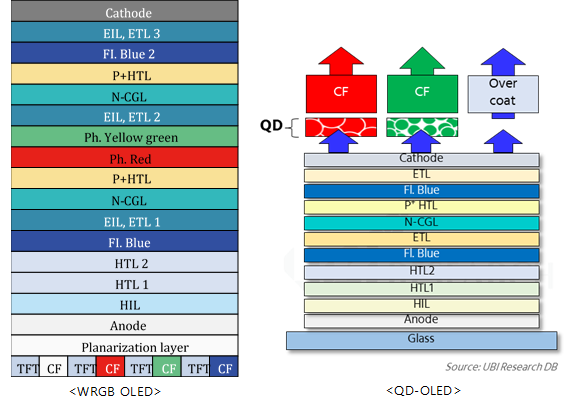
The OLED panel for TV only produces LG Display, but Samsung Display is pursuing QD-OLED commercialization using blue light emitting material and QD. In addition, although BOE is a white OLED structure similar to LG Display, it is developing a top-emission structure that transmits light in the opposite direction of TFT, and it is expected that three companies will produce OLED panels for TV within a few years, and the emitting material market is expected to increase as well.
The market for emitting materials in 2020 is expected to increase by 7% from 2019 to $ 1.37 billion. Among the emitting materials, green and red hosts are expected to be $ 19.2 billion and $ 19 billion, respectively, and green dopants and P + are expected to be $ 1.37 billion and $ 1.35 billion, respectively.