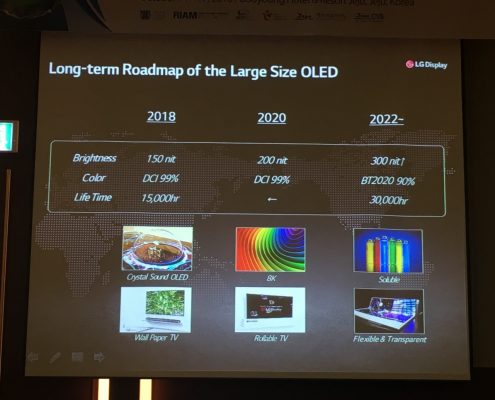
Source = UDC
Hyunjoo Kang / jjoo@olednet.com
Universal Display Corporation( UDC ), enabling energy-efficient displays and lighting with its Universal PHOLED technology and materials, today reported financial results for the second quarter ended June 30, 2016.
For the second quarter of 2016, the Company reported net income of $21.8 million, or $0.46 per diluted share, on revenues of $64.4 million. This includes $1.8 million of currency exchange loss related to the BASF OLED patent acquisition. For the second quarter of 2015, the Company reported a net loss of $11.8 million, or $0.25 per diluted share, on revenues of $58.1 million. The 2015 net loss reflected a $33.0 million write-down of inventory, primarily of an existing host material and associated work-in-process. Excluding this item and its associated $1.9 million reduction of income tax expense, adjusted net income for the second quarter of 2015 was $19.4 million, or $0.41 per diluted share (see “reconciliation of non-GAAP Measures” below for further discussion of the non-GAAP measures included in this release).
“Our second quarter 2016 revenues and net income increased year-over-year, and we maintained our strong margin profile. We are confident that the underlying growth fundamentals of our long-term outlook remain robust, but near-term, we expect our revenue growth will be delayed by about six months,” said Sidney D. Rosenblatt, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Universal Display.
Rosenblatt continued, “We expect strong revenue growth in 2017. At that time, new OLED production from the multi-year capital expenditure cycle is slated to start contributing to our revenues. Ahead of this wave of high-volume capacity, we have been working to expand and broaden our team and core competencies to advance our strategic initiatives and increase our competitive edge. We expect these initiatives, along with new OLED capacity, coupled with our pipeline of new materials, new technologies and new agreements, to bolster our long-term growth plan.”
Financial Highlights for the Second Quarter of 2016
The Company reported revenues of $64.4 million, compared to revenues of $58.1 million for the same quarter of 2015, an increase of 10.8%. Material sales were $22.3 million, down 8.3% compared to the second quarter of 2015, primarily due to a $2.0 million decline in host material sales. Royalty and license fees were $42.0 million, up from $33.7 million in the second quarter of 2015. The Company recognized $37.5 million in Samsung Display Co., Ltd. (SDC) licensing revenue in the second quarter of 2016, up from $30.0 million in the same quarter of 2015.
The Company reported operating income of $34.0 million in the second quarter of 2016, compared to an operating loss of $4.8 million for the second quarter of 2015. Excluding the inventory write-down of $33.0 million, adjusted operating income was $28.2 million for the second quarter of 2015. Operating expenses were $30.4 million, compared to $62.9 million in the second quarter of 2015 and cost of materials was $5.7 million, compared to $39.1 million in the second quarter of 2015, both of which included the inventory write-down of $33.0 million in the second quarter of 2015.
The Company’s balance sheet remained strong, with cash and cash equivalents and investments of $332.0 million as of June 30, 2016. During the second quarter, the Company added $96.0 million in intangible assets in the form of intellectual property purchases and certain other assets from BASF, increasing the portfolio to more than 4,100 issued and pending patents worldwide. During the second quarter, the Company generated $36.2 million in operating cash flow.
Financial Highlights for the First Six Months of 2016
The Company reported revenues of $94.1 million, compared to revenues of $89.3 million for the first half of 2015, or an increase of 5.4%. Material sales were $46.6 million, down 8.8% compared to $51.1 million in the first half of 2015, primarily due to a $7.0 million decline in host sales. Royalty and license fees were $47.4 million, up from $38.1 million in the first half of 2015.
The Company reported operating income of $36.7 million in the first half of 2016, compared to an operating loss of $3.1 million for the first half of 2015. Excluding the inventory write-down of $33.0 million, adjusted operating income was $30.0 million for 2015. For the first half of 2016, we reported net income of $23.8 million, or $0.51 per diluted share, compared to a net loss of $10.5 million, or $0.23 per diluted share, for the same period of 2015. Excluding the inventory write-down and the associated $1.9 million reduction of income tax expense, adjusted net income was $20.7 million, or $0.45 per diluted share, for the first half of 2015.
Operating cash flow for the first half of 2016 was $36.2 million, a decrease of 51.8% compared to $75.2 million for the first half of 2015 which included an upfront $42.0 million license and royalty payment.
2016 Guidance
While the OLED industry is still at a stage where many variables can have a material impact on its growth, based upon the most recent and best information on hand, the Company believes it is prudent to revise its 2016 revenues guidance. The Company now expects 2016 revenues to be in the range of $190 million to $200 million.