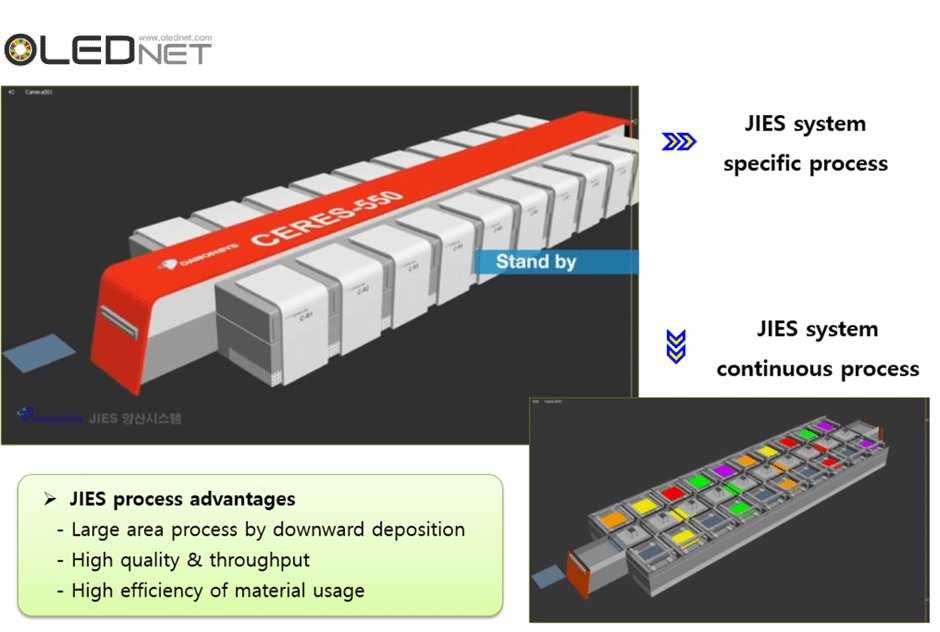
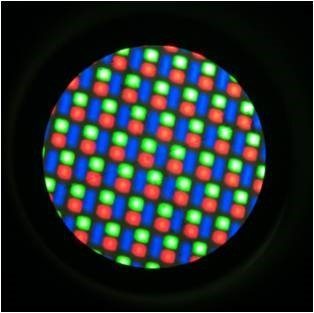
Sunic System’s solution for 11K (2,250 ppi) AMOLED production revealed in IMID 2016 held in Jeju ICC, South Korea is receiving much attention.
In the 2nd OLED Korea Conference held earlier this year, Samsung Display’s principal engineer Insun Hwang told the attendees that high resolution is the key in VR, and approximately 2,000 ppi is required for suitable realism. He explained that the resolution of VR falls as the distance between the user and display is short and this is an issue that needs to be solved.
The highest resolution of the current AMOLED panel for mobile device is 806 ppi, revealed by Samsung Display in SID 2016. The technology being applied to AMOLED panel mass production is evaporating OLED emitting materials through heat from linear source, and depositing the OLED emitting materials onto substrate through fine metal mask (FMM).
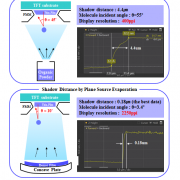
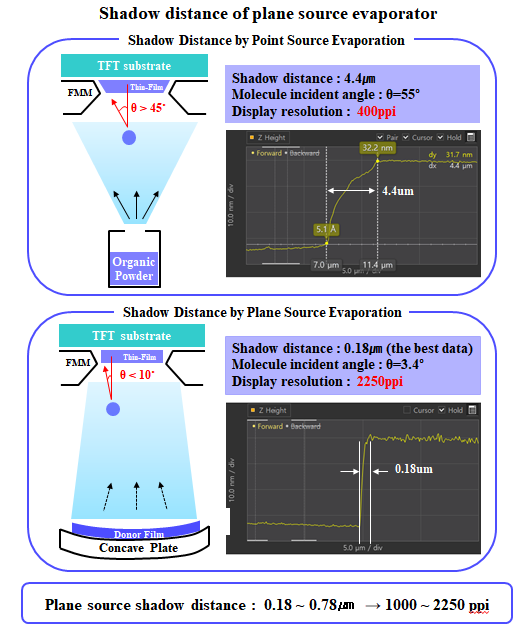
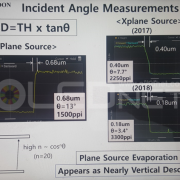
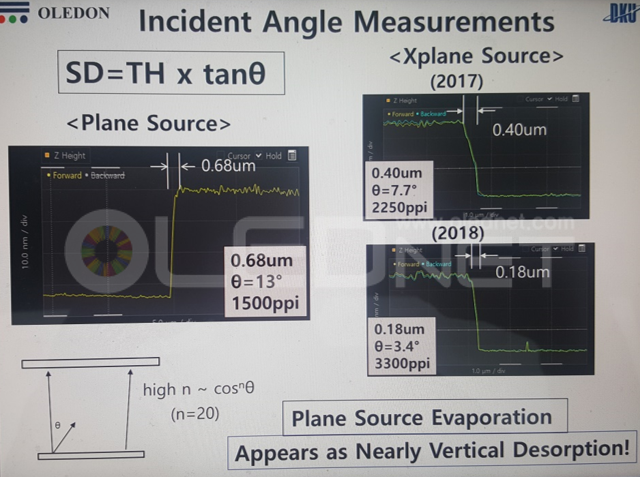
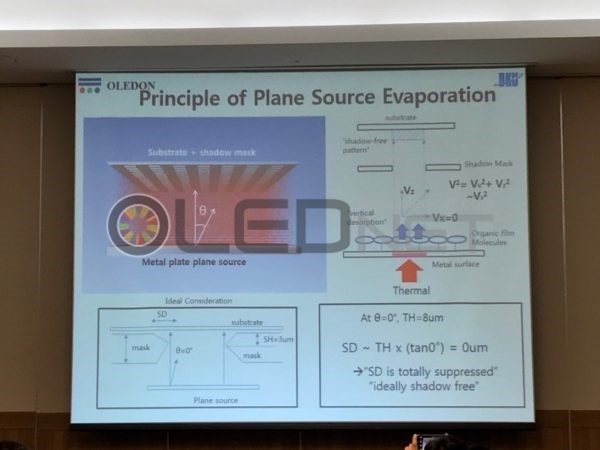
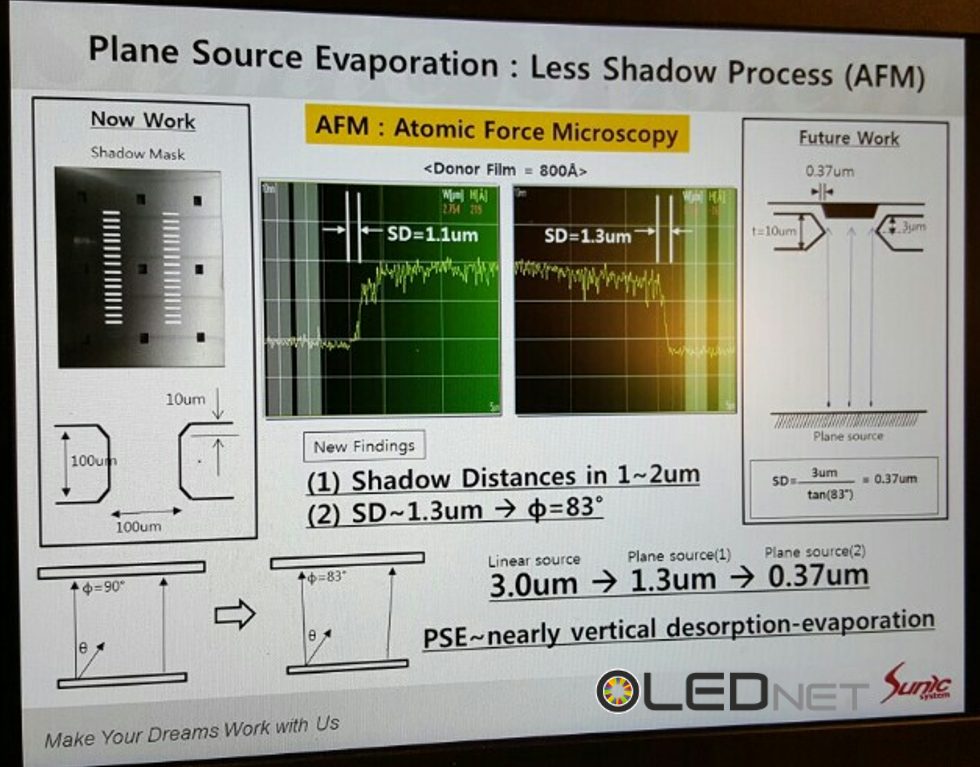
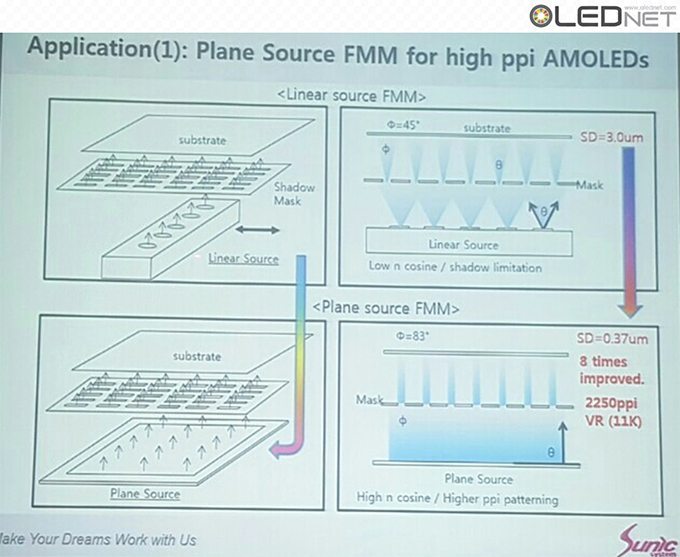
However, during the deposition stage of the OLED emitting materials, due to the distance between the evaporation source and FMM, thickness of FMM, and distance between FMM and substrate, incidence angle (θ) is produced. Due to the incidence angle, shadow distance (SD) is generated. Because of the SD issues, mask thickness and step height that minimize SD have to be decided, and these are the main reasons for the FMM production difficulty.
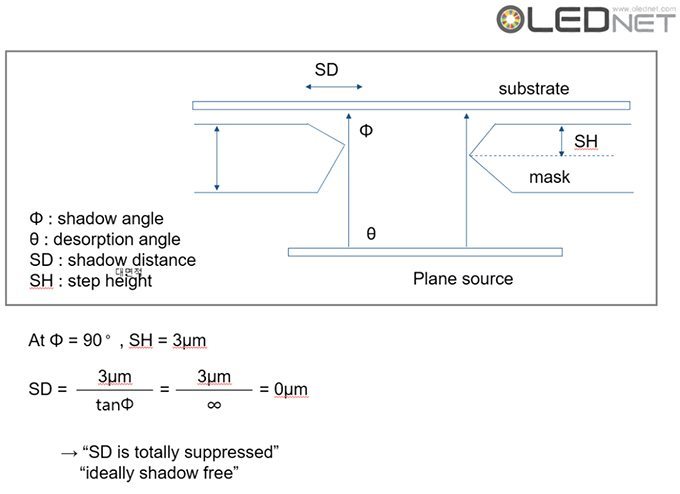
Shadow Distance Principle, Sunic System IMID 2016
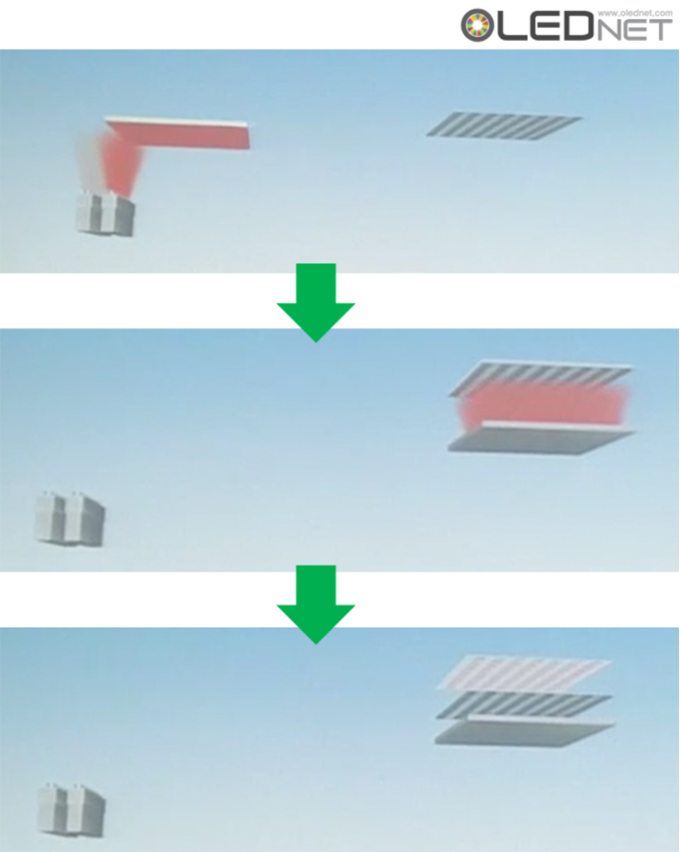
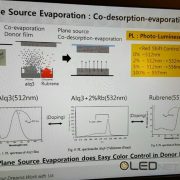
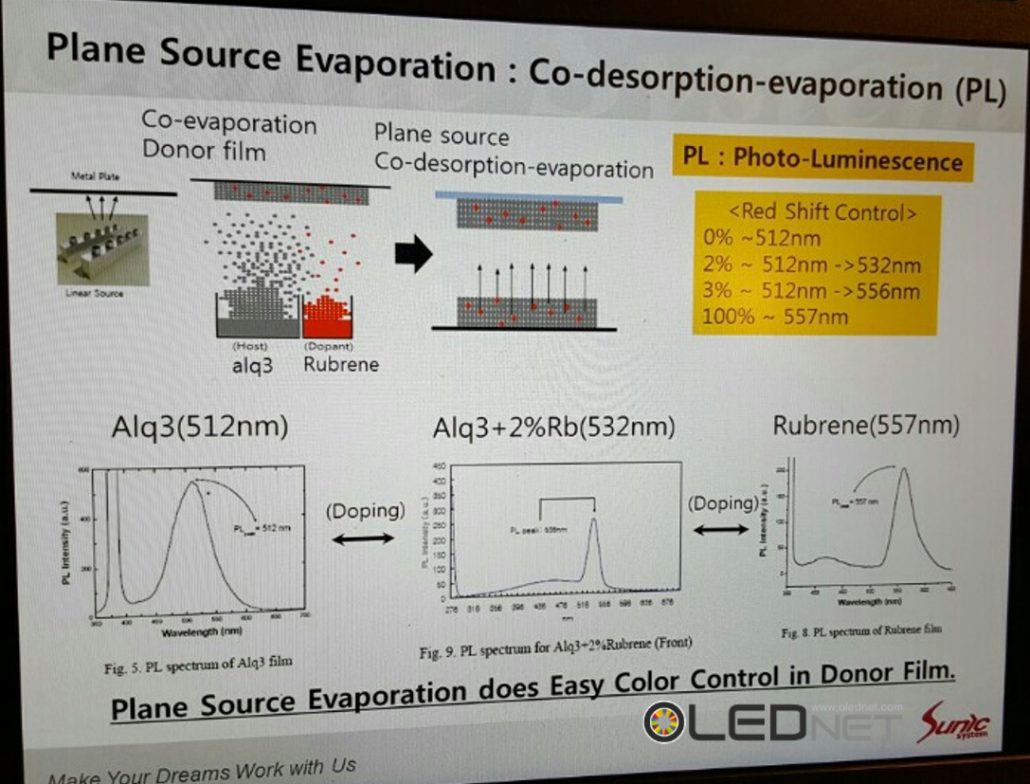
Plane Source Process, Sunic System IMID 2016
Plane Source Process, Sunic System IMID 2016

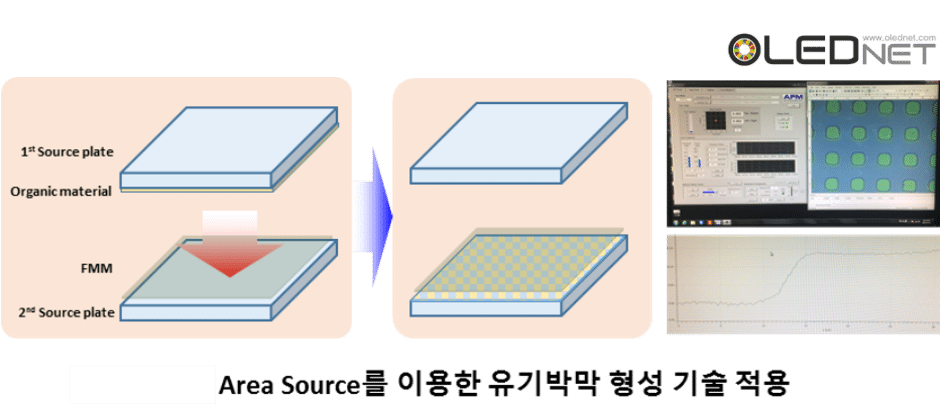
Plane Source Application, Sunic System IMID 2016
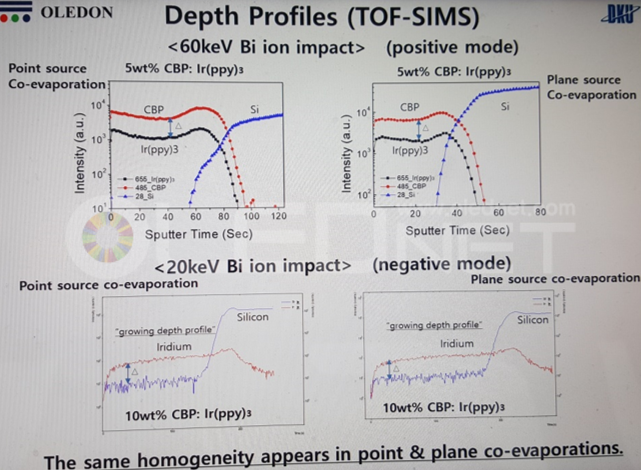
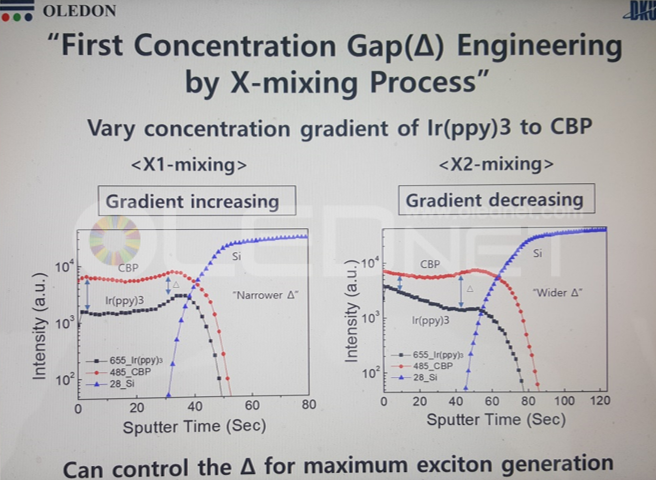
To solve these issues, Sunic System suggested plane source, instead of linear source, and reported that this will become a key technology for high resolution AMOLED panel. Plane source technology deposits OLED emitting materials on metal plate and vertically evaporates the materials through heat after reversing that metal plate. If OLED emitting material shadow angle (Ф) becomes 90, the SD (shadow distance, step height / tanФ) theoretically becomes 0. This means FMM can be designed to be thin and high resolution, allowing for high resolution AMOLED panel production.
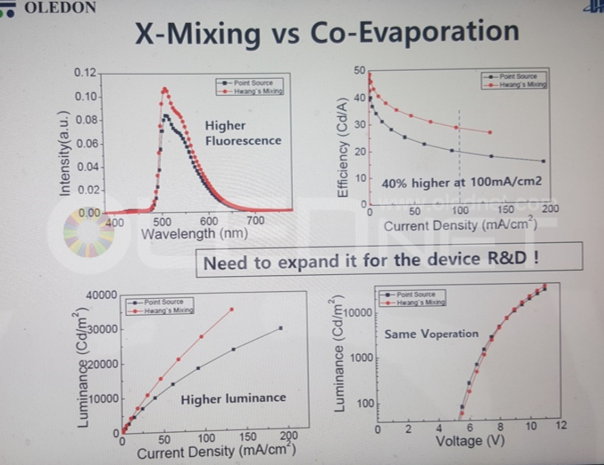
Sunic System’s Dr. Chang Hun Hwang explained that plane source can reduce SD figure up to approximately 8 times compared to existing technology, and 11K (2250 ppi) AMOLED panel for VR use becomes possible. Through this 8K (200 ppi) RGB OLED TV panel production becomes possible in large area SMS evaporation technology.
Particularly, if plane source using SMS evaporation technology can be applied to large area, it is also expected to have significant impact on large area OLED panel production technology.
So far, inkjet printing technology applied solution process method has been mainly developed for RGB large area OLED panel production, but soluble OLED emitting materials’ performance fall short of existing evaporation OLED emitting materials. However, if plane source technology is successfully developed and applied, evaporation OLED emitting materials can be used. Accordingly, this could become large size OLED panel production technology that replaces solution process OLED.
Sunic System supplied Gen6 evaporator to LG Display, a first for a Korean manufacturing equipment company, and active mass production is expected to be possible from 2018.