Recently VR contents experience through smart-phone device has been increased, therefore high resolution of smart phone is becoming necessary. However, OLED smart-phone resolution still remains at QHD level for 3 years since QHD OLED is applied to Galaxy Note 4 for the first time in 2014.
The core point that decides resolution of OLED smart-phone is evaporation process for emission layer. Bottom-up type evaporation method, which is applied to the recent devices is that substrate and FMM (fine metal mask) are horizontally arranged on the upper side of evaporator and vaporize the organic material from the lower linear source in order to form RGB layer.
Thin FMM measures less than 15um thick is necessary for making high resolution OLED like UHD level, however, as FMM gets thinner, it would be difficult to make mass production because technical problems will be occurred such as patterning, sealing and welding.
In order to solve these problems, various metal mask patterning technologies are being developed such as vertical type evaporation and plane source evaporation.
Vertical type evaporator that arranges board and FMM vertical is developed by Hitachi of Japan for the first time. And Canon Tokki exhibited Gen6 vertical type evaporator at Finetech Japan 2013, however it is not being used for mass production at the moment.

<Canon Tokki’s Gen6 vertical type evaporator which is exhibited at Finetech Japan 2013>
According to the recent ETNEWS, Applied Materials developed Gen6 flexible OLED vertical type evaporator and it is being tested in Japan Display.
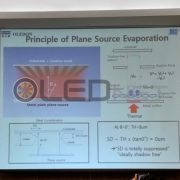
Plane source evaporator is being tested but also the linear source type. Plane source evaporator method is that an organic material is first evaporated on the metal surface to produce plane source, then re-evaporated in order to form an organic thin film on the substrate.
In the past iMiD 2017, representative of OLEDON, Chang Hoon Hwang mentioned that 2250 ppi resolution OLED can be implemented through plane source evaporator.
For metal mask patterning technology, electro forming and laser patterning technology is highlighted. Electro forming method is developed by Wave Electronics, TGO Technology, Athene and so on. Laser patterning technology is being developed by AP Systems.
As such, development for high resolution OLED is receiving great attention whether it can solve the current problems and contribute to UHD resolution implementation for OLED smart-phone.
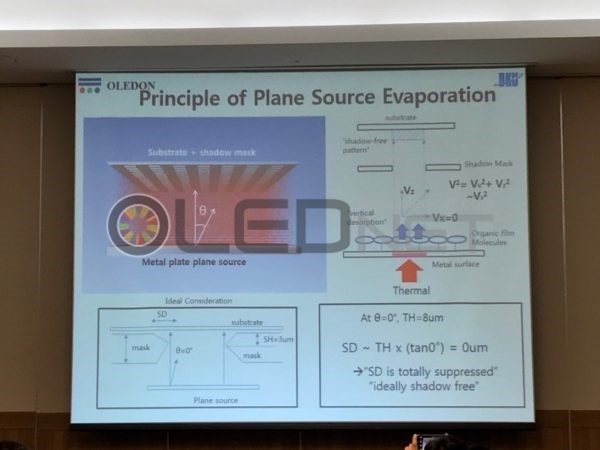
<Principle of plane source evaporation developed by OLEDON>