OLED Smartphone Launch Products Slows Down In The First Half of 2022

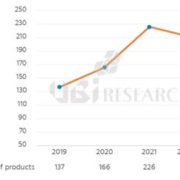
The number of OLED smartphone launches, which had steadily increased from 2019 to 2021 reached only 110 units in the first half of 2022. 137 units had been released in 2019, 166 units in 2020, and 225 units in 2021. If this industry trend continues in 2022, OLED smartphones expected release will only be similar to 2021 or even slightly fewer than it had been last year.
Most of the smartphones released in the first half of 2022 were made in China. 98 products from China accounted for 89% of market share, followed by 9 products from Korea, 2 from Japan, and 1 from India.
By size, 6.6-inch products were the most with 34 types, followed by 6.4-inch products with 31 types and 6.7-inch products with 21 types. The largest sized product was Vivo’s ‘X Fold’, which was an 8.03-inch foldable. Not including the foldables, Vivo’s ‘X Note’ was the largest at 7.0 inches. The smallest product was Sony’s ‘Xperia 10 IV’, which was 6.0 inches.
By design, 102 types of punch hole models were released, with 4 narrow bezel types, 2 notch types, and 2 UPC types. There were two types of smartphones with UPC (Under Panel Camera) applied: ZTE’s Axon 40 Ultra and Nubia Red Magic 7 Pro.

By resolution, 51 products with 300ppi range, 50 products with 400ppi range, and 9 products with 500ppi or higher were released. No products under 300ppi were released. The product with the highest resolution was Sony’s ‘Xpeia 1 IV’, which had a resolution of 643ppi.
There were three foldable phones released in the first half of the year: Vivo’s ‘X Fold’, Honor’s ‘Magic V’, and Huawei’s ‘Mate Xs2’. All three types of foldable phones have a punch-hole design. The resolution of ‘Mate Xs2’ was 424ppi, which is 10ppi higher than the average OLED smartphones released in the first half of the year. Whereas ‘X Fold’ and ‘Magic V’ were two products with the lowest resolution among OLED smartphones released in the first half of the year.